| Heptadécane
|

|
 |
| Représentations de l'heptadécane |
| Identification |
| Nom UICPA
|
Heptadécane
|
| Synonymes
|
n-heptadécane
|
| No CAS
|
629-78-7
|
| No ECHA
|
100.010.100 |
| No CE
|
211-108-4
|
| SMILES
|
|
| InChI
|
InChI : vue 3D InChI=1/C17H36/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-16-14-12-10-8-6-4-2/h3-17H2,1-2H3 |
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule
|
C17H36 [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire[1]
|
240,467 7 ± 0,016 1 g/mol
C 84,91 %, H 15,09 %,
|
| Propriétés physiques |
| T° fusion
|
22 °C
|
| T° ébullition
|
301,1 °C [2]
|
| Masse volumique
|
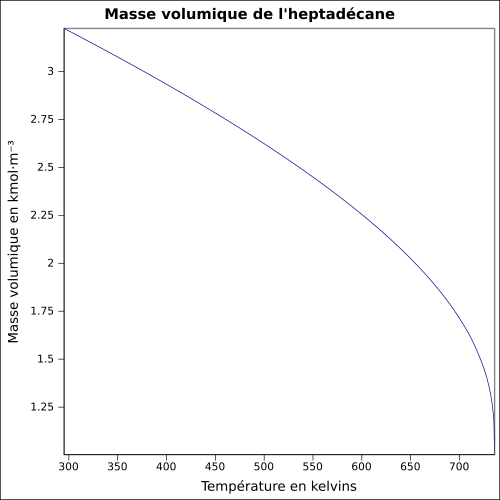
équation[3] : 
Masse volumique du liquide en kmol·m-3 et température en kelvins, de 295,13 à 736 K.
Valeurs calculées :
0,77338 g·cm-3 à 25 °C.
| T (K) |
T (°C) |
ρ (kmol·m-3) |
ρ (g·cm-3) |
|---|
| 295,13 |
21,98 |
3,2241 |
0,77531 |
| 324,52 |
51,37 |
3,14516 |
0,75633 |
| 339,22 |
66,07 |
3,105 |
0,74667 |
| 353,91 |
80,76 |
3,06432 |
0,73689 |
| 368,61 |
95,46 |
3,02311 |
0,72698 |
| 383,3 |
110,15 |
2,98132 |
0,71693 |
| 398 |
124,85 |
2,93892 |
0,70673 |
| 412,7 |
139,55 |
2,89586 |
0,69638 |
| 427,39 |
154,24 |
2,85209 |
0,68585 |
| 442,09 |
168,94 |
2,80755 |
0,67514 |
| 456,78 |
183,63 |
2,76218 |
0,66423 |
| 471,48 |
198,33 |
2,71591 |
0,6531 |
| 486,17 |
213,02 |
2,66865 |
0,64174 |
| 500,87 |
227,72 |
2,62031 |
0,63011 |
| 515,57 |
242,42 |
2,57077 |
0,6182 |
|
| T (K) |
T (°C) |
ρ (kmol·m-3) |
ρ (g·cm-3) |
|---|
| 530,26 |
257,11 |
2,51991 |
0,60597 |
| 544,96 |
271,81 |
2,46756 |
0,59338 |
| 559,65 |
286,5 |
2,41353 |
0,58039 |
| 574,35 |
301,2 |
2,35759 |
0,56694 |
| 589,04 |
315,89 |
2,29945 |
0,55296 |
| 603,74 |
330,59 |
2,23875 |
0,53836 |
| 618,43 |
345,28 |
2,17499 |
0,52303 |
| 633,13 |
359,98 |
2,10755 |
0,50681 |
| 647,83 |
374,68 |
2,03552 |
0,48949 |
| 662,52 |
389,37 |
1,95759 |
0,47075 |
| 677,22 |
404,07 |
1,87171 |
0,45009 |
| 691,91 |
418,76 |
1,77432 |
0,42668 |
| 706,61 |
433,46 |
1,65827 |
0,39877 |
| 721,3 |
448,15 |
1,50404 |
0,36168 |
| 736 |
462,85 |
1,002 |
0,24095 |
|
|
| Pression de vapeur saturante
|
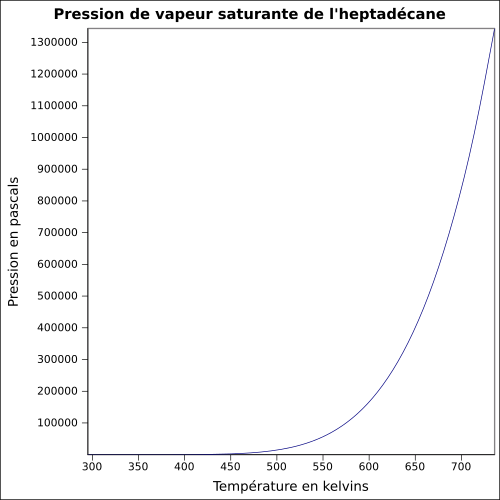
équation[3] : 
Pression en pascals et température en kelvins, de 295,13 à 736 K.
Valeurs calculées :
0,07 Pa à 25 °C.
| T (K) |
T (°C) |
P (Pa) |
|---|
| 295,13 |
21,98 |
0,047 |
| 324,52 |
51,37 |
1,02 |
| 339,22 |
66,07 |
3,76 |
| 353,91 |
80,76 |
12,05 |
| 368,61 |
95,46 |
34,41 |
| 383,3 |
110,15 |
88,81 |
| 398 |
124,85 |
209,69 |
| 412,7 |
139,55 |
457,95 |
| 427,39 |
154,24 |
933,56 |
| 442,09 |
168,94 |
1 790,61 |
| 456,78 |
183,63 |
3 253,6 |
| 471,48 |
198,33 |
5 634,02 |
| 486,17 |
213,02 |
9 345,83 |
| 500,87 |
227,72 |
14 919 |
| 515,57 |
242,42 |
23 010,3 |
|
| T (K) |
T (°C) |
P (Pa) |
|---|
| 530,26 |
257,11 |
34 411,11 |
| 544,96 |
271,81 |
50 052,68 |
| 559,65 |
286,5 |
71 009,15 |
| 574,35 |
301,2 |
98 499,52 |
| 589,04 |
315,89 |
133 889,48 |
| 603,74 |
330,59 |
178 694,41 |
| 618,43 |
345,28 |
234 584,59 |
| 633,13 |
359,98 |
303 393,75 |
| 647,83 |
374,68 |
387 131,91 |
| 662,52 |
389,37 |
488 003,49 |
| 677,22 |
404,07 |
608 431,34 |
| 691,91 |
418,76 |
751 087,59 |
| 706,61 |
433,46 |
918 931,97 |
| 721,3 |
448,15 |
1 115 258,65 |
| 736 |
462,85 |
1 343 800
|
|
 |
| Point critique
|
1 340 kPa [4], 462,85 °C [2]
|
| Thermochimie |
| Cp
|
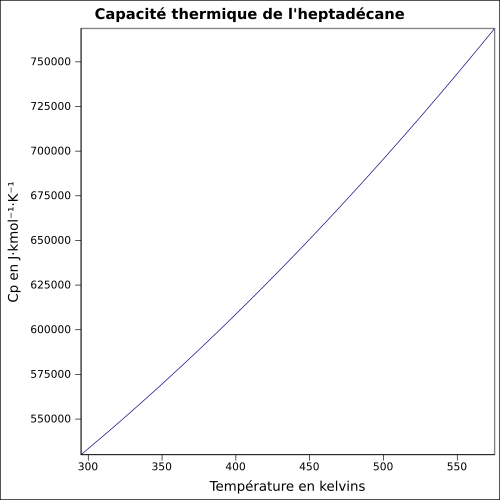
équation[3] : 
Capacité thermique du liquide en J·kmol-1·K-1 et température en kelvins, de 295,13 à 575,3 K.
Valeurs calculées :
532,137 J·mol-1·K-1 à 25 °C.
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
|---|
| 295,13 |
21,98 |
530 050 |
2 204 |
| 313 |
39,85 |
542 557 |
2 256 |
| 323 |
49,85 |
549 717 |
2 286 |
| 332 |
58,85 |
556 260 |
2 313 |
| 341 |
67,85 |
562 898 |
2 341 |
| 351 |
77,85 |
570 382 |
2 372 |
| 360 |
86,85 |
577 217 |
2 400 |
| 369 |
95,85 |
584 146 |
2 429 |
| 379 |
105,85 |
591 955 |
2 462 |
| 388 |
114,85 |
599 082 |
2 491 |
| 397 |
123,85 |
606 302 |
2 521 |
| 407 |
133,85 |
614 435 |
2 555 |
| 416 |
142,85 |
621 854 |
2 586 |
| 425 |
151,85 |
629 366 |
2 617 |
| 435 |
161,85 |
637 824 |
2 652 |
|
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
|---|
| 444 |
170,85 |
645 534 |
2 684 |
| 453 |
179,85 |
653 338 |
2 717 |
| 463 |
189,85 |
662 120 |
2 753 |
| 472 |
198,85 |
670 122 |
2 787 |
| 481 |
207,85 |
678 218 |
2 820 |
| 491 |
217,85 |
687 323 |
2 858 |
| 500 |
226,85 |
695 618 |
2 893 |
| 509 |
235,85 |
704 005 |
2 928 |
| 519 |
245,85 |
713 435 |
2 967 |
| 528 |
254,85 |
722 021 |
3 003 |
| 537 |
263,85 |
730 701 |
3 039 |
| 547 |
273,85 |
740 455 |
3 079 |
| 556 |
282,85 |
749 332 |
3 116 |
| 565 |
291,85 |
758 304 |
3 153 |
| 575,3 |
302,15 |
768 690 |
3 197 |
|
équation[5] : 
Capacité thermique du gaz en J·mol-1·K-1 et température en kelvins, de 200 à 1 500 K.
Valeurs calculées :
406,777 J·mol-1·K-1 à 25 °C.
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
|---|
| 200 |
−73,15 |
309 997 |
1 289 |
| 286 |
12,85 |
394 961 |
1 642 |
| 330 |
56,85 |
437 453 |
1 819 |
| 373 |
99,85 |
478 077 |
1 988 |
| 416 |
142,85 |
517 637 |
2 153 |
| 460 |
186,85 |
556 855 |
2 316 |
| 503 |
229,85 |
593 813 |
2 469 |
| 546 |
272,85 |
629 303 |
2 617 |
| 590 |
316,85 |
663 996 |
2 761 |
| 633 |
359,85 |
696 238 |
2 895 |
| 676 |
402,85 |
726 776 |
3 022 |
| 720 |
446,85 |
756 218 |
3 145 |
| 763 |
489,85 |
783 204 |
3 257 |
| 806 |
532,85 |
808 420 |
3 362 |
| 850 |
576,85 |
832 406 |
3 462 |
|
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
|---|
| 893 |
619,85 |
854 108 |
3 552 |
| 936 |
662,85 |
874 142 |
3 635 |
| 980 |
706,85 |
892 992 |
3 713 |
| 1 023 |
749,85 |
909 892 |
3 784 |
| 1 066 |
792,85 |
925 397 |
3 848 |
| 1 110 |
836,85 |
939 951 |
3 909 |
| 1 153 |
879,85 |
953 043 |
3 963 |
| 1 196 |
922,85 |
965 182 |
4 014 |
| 1 240 |
966,85 |
976 807 |
4 062 |
| 1 283 |
1 009,85 |
987 596 |
4 107 |
| 1 326 |
1 052,85 |
998 042 |
4 150 |
| 1 370 |
1 096,85 |
1 008 626 |
4 194 |
| 1 413 |
1 139,85 |
1 019 129 |
4 238 |
| 1 456 |
1 182,85 |
1 030 068 |
4 284 |
| 1 500 |
1 226,85 |
1 042 021 |
4 333 |
|
|
|
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. |
modifier  |


