Atlas of Afghanistan

|
Wikimedia Commons Atlas of the World The Wikimedia Atlas of the World is an organized and commented collection of geographical, political and historical maps available at Wikimedia Commons. Discussion • Update the atlas • Index of the Atlas • Atlas in categories • Other atlases on line |
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General maps

|
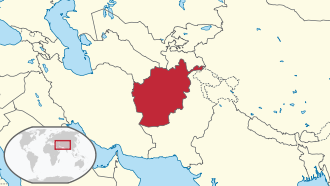
Map of Afghanistan |

|
Map of Afghanistan |

|
Topographic map of Afghanistan |
Maps of divisions
This section holds maps of the administrative divisions.

|
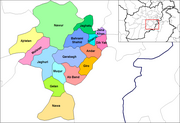
Provinces of Afghanistan |

|
Provinces of Afghanistan (in Pashto) |

|
Provinces of Afghanistan (in Dari) |

|
Districts of Afghanistan |

|
Districts of Afghanistan |
-
Districts of Badakhshan
-
Districts of Badghis
-
Districts of Baghlan
-
Districts of Balkh
-
Districts of Bamyan
-
Districts of Daykundi
-
Districts of Farah
-
Districts of Faryab
-
Districts of Ghazni
-
Districts of Ghor
-
Districts of Helmand
-
Districts of Herat
-
Districts of Jowzjan
-
Districts of Kabul
-
Districts of Kandahar
-
Districts of Kapisa
-
Districts of Khost
-
Districts of Konar
-
Districts of Kunduz
-
Districts of Laghman
-
Districts of Lowgar
-
Districts of Nangarhar
-
Districts of Nimruz
-
Districts of Nurestan
-
Districts of Oruzgan
-
Districts of Paktia
-
Districts of Paktika
-
District of Panjshir
-
Districts of Parvan
-
Districts of Samangan
-
Districts of Sare Pol
-
Districts of Takhar
-
Districts of Wardak
-
Districts of Zabol
History maps
This section holds a short summary of the history of the area of present-day Afghanistan, illustrated with maps, including historical maps of former countries and empires that included present-day Afghanistan.
Early history
| Present-day Afghanistan is around 1500 and 800 BC part of Ariana. |
Persian rule
| 6th century BCE-328 BCE: Achaemenid Empire - occupying country ► Iran |

|
Ariana is conquered by Persia in the sixth century BC. This map shows the Achaemenid Empire (Persia (648–330 BCE) at its greatest extent. Ariana becomes a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire. |
Macedonian rule

|
328 BCE-323 BCE: Macedonian Empire - occupying country ► Macedonian Empire |

|
In 328 BC, Alexander the Great of Macedon enters the territory to capture Bactria. This map shows the Expedition of Alexander the Great 334-323 BCE |

|
Hellenistic successor states: Kingdom of Ptolemy Kingdom of Cassander Kingdom of Lysimachus Kingdom of Seleucus Other states:
|

|
Hellenistic world in 200 BCE |

|
Greco-Bactrian kingdom (250-125 BCE) |

|
Indo-Greek kingdom (180 BCE-10 AD) |

|
Indo-Greek Kingdom |

|
Bactria |
| Invasions by the Scythians, White Huns and Turkic tribes follow in succeeding centuries. Mentionable is the rule since the first century by the Kushanas, a buddhist people. |

|
Kushan Empire |

|
Hephthalite dominion (520) |

|
Harsha's Empire around 600 |
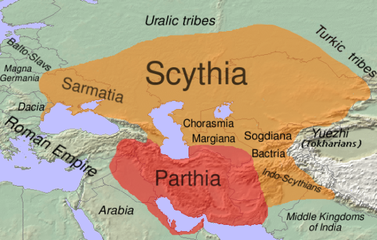
| The Parthian Empire (250 BCE-226 CE) |
|
Map of Parthia 100 BC |

|
Indo-Sassanide Empire |
| The Persian Sassanian Empire (226-650) in 602 to 629, Strokes: Under Sassanid military control. |

|
Sassanide Empire |

|
Sassanide Empire |

|
In 642 the Caliphate invades the entire region and introduces islam. Expansion of the Caliphate: I: Muhammad; II: Abu Bakr; III: Omar and IV: Othman |

|
Age of the Caliphs |

|
Caliphate around 750 |
| The rule of the Caliphate is replaced by a temporary Persian rule until the area is conquered by the Turkic Ghaznavids in 998. Ghazni is turned into a great cultural center as well as a base for frequent forays into India. |

|
Various princes attempt to rule sections of the country until the Mongol invasion of 1219 led by Genghis Khan. Map showing changes in borders of the Mongol Empire from founding by Genghis Khan in 1206, Genghis Khan's death in 1227 to the rule of Kublai Khan (1260–1294). (Uses modern day borders)
Mongol Empire
By 1294 the empire had split into: Empire of the Great Khan (Yuan Dynasty)
|
| Following Genghis Khan's death in 1227, a succession of chiefs and princes struggle for supremacy until late in the 14th century, when one of his descendants, Tamerlane, incorporates Afghanistan into his own vast Asian empire. Babur, a descendant of Tamerlane and the founder of India's Mogul dynasty at the beginning of the 16th century, makes Kabul the capital of an Afghan principality. |

|
Mughal Empire (1600) and European possesions |

|
Mughal Empire (1700) and Maratha Confederacy (1860) |

|
Mughal Empire (1526-1857) |

|
Mughal Empire |

|
In 1747 Afghanistan liberates itself from the Empire of the Great Mogul. The State of Afghanistan is formed and Ahmad Shah Durrani establishes his rule. Throughout his reign, Durrani consolidates chieftainships, petty principalities and fragmented provinces into one country. His rule extends from Mashad in the west to Kashmir and Delhi in the east, and from the Amu Darya (Oxus) River in the north to the Arabian Sea in the south. From time to time separate Afghan states are installed in Kandahar and Herat. Though the country is united sincethen, it has to accept after the second Anglo-Afghan war (1878-80), that brings Amir Abdur Rahman to the throne, a British protectorate in 1881. The British retain effective control over Kabul's foreign affairs.
After the third Anglo-Afghan war in 1919, Britain relinquishes its control over Afghan foreign affairs by signing the Treaty of Rawalpindi. This means full independence of Afghanistan and the establishment of a more or less constitutional monarchy. King Amanullah (1919-29) renames the country Kingdom of Afghanistan in 1926 and introduces modernization and secularization. This leads to his assassination and a short civil war. In 1929 Nadir Shah becomes king. Four years later, however, he is assassinated in a revenge killing by a Kabul student. In 1933 Mohammed Zahir Shah becomes king. He introduces in 1964 a liberal constitution providing for a two-chamber legislature to which the king appointed one-third of the deputies. The people elected another third, and the remainder were selected indirectly by provincial assemblies. He permits a multi-party system. This leads to the formation of the communist Hizb-i-Democratic-i-Khalq (People's Democratic Party, HDK), which had close ideological ties to the Soviet Union. In 1967, the PDPA split into two major rival factions: the Khalq (Masses) faction headed by Noo Mohammad Taraki and Hafizullah Amin and supported by elements within the military, and the Parcham (Banner) faction led by Babrak Karmal. After a coup d'état in 1973 Afghanistan becomes a dictatorial republic and is renamed Republic of Afghanistan. Mohammed Daoud Khan, until that moment prime minister, becomes president. In 1978 the HDK seizes power and a communist dictatorship is established under the HDK, lead by Noor Mohammed Tarraki (1978-1979). The country is renamed Democratic Republic of Afghanistan. When Taraki is assasinated in 1979 he is succeeded by Hafizullah Amin (1979). At that moment the USSR invades the country and installs after the assasination of Amin Babrak Karmal as new president. Islamic factions start a guerilla war against the regime and the soviet-occupation. In an attempt to moderate Afghanistan is renamed into Republic of Afghanistan in 1987. Karmal is replaced by Mohammed Najibullah in 1986. In 1990 the Islamic mujaheddin (Holy Warriors) expel the communist dictatorship. Though a central government is installed, de facto the country is ruled by warlords. In 1992 the central government renames the country into the Islamic State of Afghanistan. Burhanuddin Rabbani becomes president. The civil war continues and in 1996 the Taleban movement of spiritual leader Mullah Mohammad Omar seizes power in most of the country. Afghanistan becomes a theocratic dictatorship and is renamed Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. Mullah Mohammad Rabbani is appointed president. After an invasion by the United States in 2001, followed by a popular uprising, the dictatorship collapses. Afghanistan gets a transition governement and is renamed Islamic State of Afghanistan. Burhanuddin Rabbani resumes office, but the same year he is succeeded by Hamid Karzai. In 2004 a new constitution is accepted, identifying Afghanistan as an "Islamic Republic." The constitution paves the way for nationwide presidential and parliamentary elections to be held in june 2004. The government's authority beyond the capital, Kabul, is slowly growing, although its ability to deliver necessary social services remains largely dependent on funds from the international donor community. |

|
Communist invasion of Afghanistan |

|
Afghanistan just before the US invasion |

|
Provinces until 2004 |
Old maps
This section holds copies of original general maps more than 70 years old.

|
Hindustan in 1812 by Arrowsmith and Lewis |

|
Map of Central Asia from Meyers Konversationslexikons (1885-1900), showing what is now Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and parts of Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Chin |
Other maps

|
Ethhno-Linguistic map of Afghanistan |

|
Provincial Reconstruction Teams |
Notes and references
|
General remarks:
|