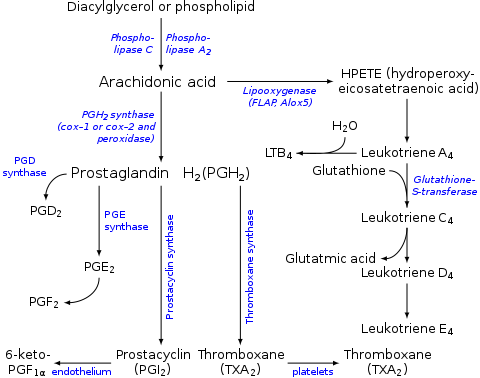
Leukotriene D4 (LTD4) is one of the leukotrienes. Its main function in the body is to induce the contraction of smooth muscle, resulting in bronchoconstriction and vasoconstriction. It also increases vascular permeability. LTD4 is released by basophils. Other leukotrienes that function in a similar manner are leukotrienes C4 and E4. Pharmacological agents that inhibit the function of these leukotrienes are leukotriene receptor antagonists (e.g., zafirlukast, montelukast) and are useful for asthmatic individuals.[1]

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
(5S,6R,7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-6-({(2R)-2-Amino-3-[(carboxymethyl)amino]-3-oxopropyl}sulfanyl)-5-hydroxyicosa-7,9,11,14-tetraenoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Leukotriene+D4 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H40N2O6S | |
| Molar mass | 496.66 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ "Montelukast (Monograph)". drugs.com.